CONTENTS
Fungal Acne Unveiled: Everything You Need to Know
As skincare enthusiasts continue to dig deep into the world of skin issues, fungi are starting to steal the show. One of the most prevalent conditions that have been getting many buzzes lately is fungal acne.
Unfortunately, fungal acne is often misdiagnosed and left untreated, causing havoc on the skin. Read on! Ahead, we will unveil the mystery behind this pesky condition and give you all the information you need to know.
What is Fungal Acne?
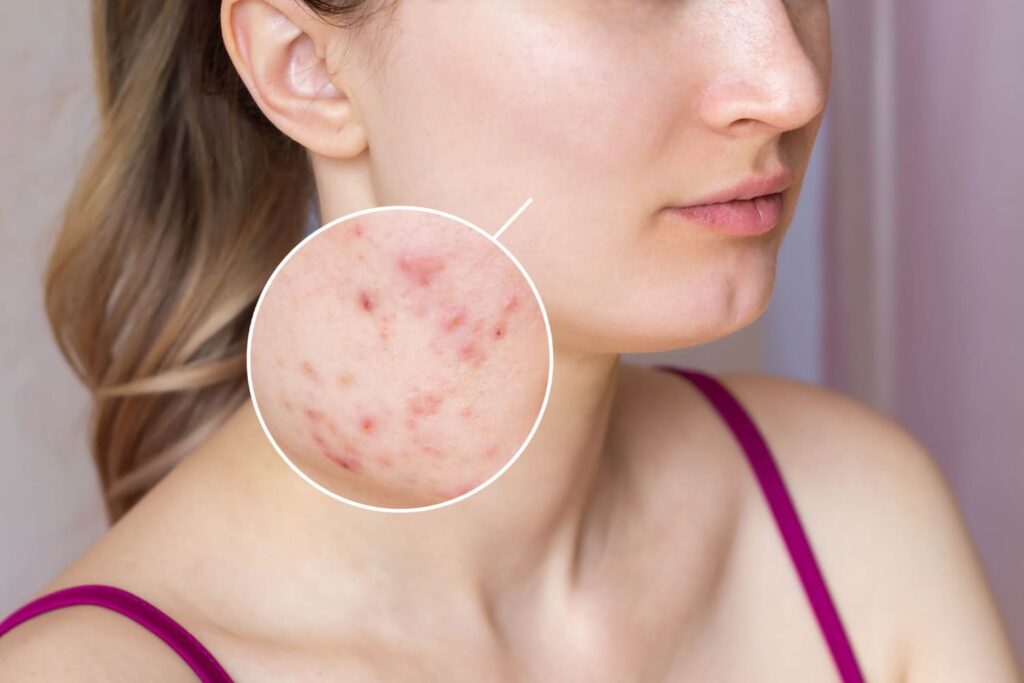
Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is a skin condition often misdiagnosed as acne vulgaris (traditional acne). Still, it’s actually caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin.
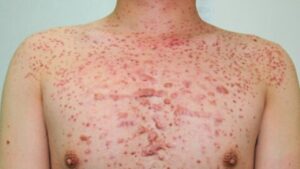
This fungal infection commonly appears on the chest, back, shoulders, and neck and can manifest as tiny bumps or pustules (yellow pus) that resemble acne.
While regular acne is caused by bacteria, this acne type is caused by a specific type of yeast called Malassezia. This type of yeast is present on everyone’s skin, but it can cause inflammation and breakouts when it overgrows.
What are the Symptoms of Fungal Acne?

The symptoms of this condition can vary from person to person but most commonly appear as small papules (red bumps) or pustules (yellow pus) when they get larger. These bumps may be itchy or tender and can be concentrated in specific areas such as the chest, back, and face.
Several symptoms, such as redness, flakiness, or a burning sensation, may also occur.
What Causes Fungal Acne on Your Face?

Fungal acne on your face is caused by a yeast overgrowth called Malassezia, which is naturally present on everyone’s skin.
Malassezia feeds on oil produced by your skin’s sebaceous glands, leading to an imbalance in the skin’s ecosystem. When the yeast overgrows within the hair follicles, it can cause inflammation, resulting in breakouts or skin irritation.
Certain factors can contribute to the development of this acne type on the face, such as a weakened immune system, excessive sweating, and hot and humid weather.
Other factors include using oil-based or heavy skincare products, which can contribute to the buildup of oil on the skin leading to an increased risk of breakouts.
How is Fungal Acne Diagnosed?

This condition can be challenging to diagnose as it often looks very similar to traditional acne, making a proper diagnosis crucial to effective treatment.
To diagnose this condition, a dermatologist may perform a skin scraping and then examine it under a microscope to identify the type of yeast responsible for the symptoms. They may also take a sample of the skin cells to test for the presence of the Malassezia yeast.
An accurate diagnosis is vital to effective treatment. If you suspect you have one, it is essential to seek professional medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How is Fungal Acne Treated?

You can effectively treat this condition with both topical and oral antifungal medications. Topical treatments include antifungal creams, such as ketoconazole, sulfur products, and azelaic acid, which can help to decrease fungal growth on the skin.
Additionally, a gentle skincare routine using oil-free and non-comedogenic products can help to treat this acne type and prevent future breakouts.
Oral medications, such as itraconazole or fluconazole, may also be prescribed in severe cases or if topical treatments are ineffective. It’s important to note that proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing this acne type.
Side Effects of Antifungal Acne Treatment

Although antifungal acne treatments are generally safe and effective, they can sometimes have side effects.
Common side effects of topical antifungal creams can include mild irritation, itching, or burning, while oral medications may cause headaches or gastrointestinal upset.
In rare cases, both topical and oral antifungal treatments can cause an allergic reaction, which may lead to more severe side effects.
To minimize the risk of side effects, following your dermatologist’s instructions when using antifungal acne treatments is essential. If you experience side effects, it’s essential to contact your healthcare provider right away for advice.
Fungal Acne Vs. Regular Acne

Fungal and regular acne share some similarities, but different factors cause them and require different treatments.
Bacteria typically cause regular acne, while yeast overgrowth on the skin causes fungal acne. Also, regular acne often appears as papules, blackheads, or whiteheads, while fungal acne tends to look like small, itchy pustules.
Additionally, regular acne can occur anywhere but is commonly found on the face, chest, and back. In contrast, fungal acne is usually found on the chest, shoulders, neck, and back, though it can also appear on the forehead, temples, and frontal hairline.
Traditional acne treatments may not work for fungal acne and can actually worsen the condition, while antifungal treatments are effective for treating fungal acne.
If you’re unsure what kind of acne you have, it’s important to see your dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does fungal acne ever go away?
Yes, it can be effectively treated and managed; in most cases, it will go away with proper treatment. Typically, it takes a few weeks to a few months to go away. They can clear up differently for each person depending on the condition and the effectiveness of the treatment used.
What should I avoid with fungal acne?
Avoid using oil-based and heavy skincare and hair care products, touching or picking at the affected areas on your skin, and wearing tight clothing or fabrics that trap moisture, such as polyester or spandex. Those actions can contribute to the growth of yeast.
Is salicylic acid good for fungal acne?
While salicylic acid may have some benefits for traditional acne, it can make fungal acne worse by causing dryness and stripping the skin’s natural oils, which can lead to increased yeast growth.
If you suspect you have one, you can use an over-the-counter antifungal cream or seek professional medical advice right away for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan.
Conclusion
Fungal acne can be quite a tricky problem to solve, but knowledge is power. Whether picking up the right antifungal products or shopping for antifungal agents like clotrimazole, you have everything you need at your fingertips to get rid of your acne.
Now that you know more about what causes and worsens this condition, you can make smarter decisions regarding your beauty routine, diet, and lifestyle habits. And don’t forget to visit your dermatologist to put a stop to your acne before it takes hold.
With all this information, you can now take charge of your skin health and enjoy brighter and clearer days ahead!


